Table of Content
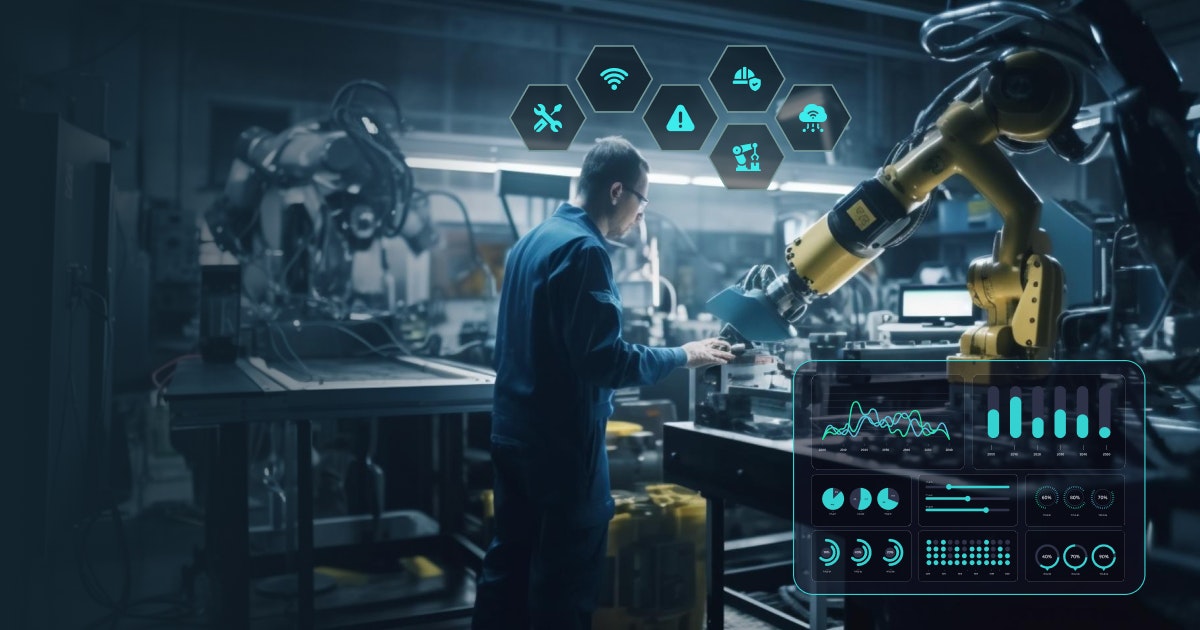
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of connected devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, enabling them to collect and exchange data over the Internet. These devices can range from simple sensors to complex machines and can be used in various applications, including industrial settings.
One of the key benefits of IoT in an industrial setting is its ability to support predictive maintenance. It is a strategy that uses data from sensors and other sources to predict when equipment will likely fail, allowing maintenance teams to intervene before a breakdown occurs.
IoT devices can collect data on a wide range of variables, such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and more, providing valuable insights into the health and performance of equipment. By analyzing this data, maintenance teams can identify patterns and trends indicating an impending failure and take corrective action before the equipment breaks down.
Exploring the concept of industrial downtime
Industrial downtime refers to when a piece of equipment or a manufacturing process is not operating as intended. Downtime can occur for various reasons, such as equipment breakdowns, scheduled maintenance, changeovers, and more. During this period, production stops, and output is lost, resulting in reduced efficiency and increased costs.
Types of industrial downtime
In many cases, downtime is a planned part of a production schedule, and it can be managed and minimized through effective planning and scheduling. However, unplanned downtime, such as that caused by equipment breakdowns or other unexpected events, can be much more disruptive and costly.
Why does industrial downtime occur?
Regardless of the underlying reason, the impact of industrial downtime is substantial. Due to the inherent interconnectedness of manufacturing processes, any major or minor disturbance can significantly influence the entire supply chain. Here are some of the causes:
1. Human error
Improper operation or misjudgment may result in equipment damage or system malfunction, ultimately leading to downtime. Occasionally, employee mistakes contribute to workplace incidents that necessitate equipment shutdown or other production methods. These actions can be either accidental or deliberate.
Regardless of the cause, human error is among the most prevalent reasons for unplanned downtime. Instances like accidentally deleting data, unplugging cables, or failing to adhere to standard protocols can all result in expensive downtime.
2. Cyberattacks
Ransomware and phishing attacks rank among the most dangerous and prevalent sources of IT downtime. Cybercriminals can easily exploit network vulnerabilities, infiltrate systems, and access sensitive data.
Ransomware attacks involve capturing and holding data hostage until victims pay for its release, allowing work to resume. Nearly 80% of manufacturers have been targeted by cyberattacks, with 47% of those attacks resulting in operational downtime.
3. Power outages
Power outages can cause production lines to stop, machinery to cease operation, and critical systems to malfunction, leading to lost production time, unmet deadlines, and increased expenses.
4. Lack of agility
An inflexible supply chain struggles to react swiftly to disruptions. This lack of agility can be attributed to many factors, including unclear and ineffective strategies, as well as subpar systems, such as:
- Inability to adjust demand
- Suboptimal logistics models
- Inaccurate demand forecasting
- Inefficient sourcing and procurement
- Inability to quickly scale the workforce
The rigidity of your supply chain can result in slower and less coordinated responses, prolonging downtime and increasing costs.
5. Material shortages
This interrupts the supply chain and restricts the accessibility of essential materials required for production. Exhausting available inventory, spare parts, or other resources such as fuel can hinder the manufacturing process and result in downtime. Additionally, power or utility outages can disrupt workflow and cause downtime as well.
6. Equipment malfunctions
On average, manufacturers face 800 hours of equipment downtime annually, and one of the reasons for that is equipment failure. While sometimes the issue originates from the machine, it often stems from improper use or inadequate monitoring and maintenance practices. Large machinery often experiences considerable stress, making it susceptible to overheating, wear and tear, and general malfunctions.
7. Device misconfiguration
When devices are not configured correctly, it can create security vulnerabilities within the network, increasing the risk of cyberattacks. Such errors can stem from several sources, such as incorrect settings, outdated software, or improper implementation of security protocols.
A Complete Guide On IOT And Industrial Internet of Things [IIOT]
Read NowThe consequences of industrial downtime
On average, manufacturers face around 800 hours of downtime annually, resulting in a substantial financial burden. Also, even though assigning a specific monetary value to downtime costs is challenging, one industry estimate suggests a staggering $22,000 per minute.
In addition, manufacturers unprepared for downtime must also grapple with other consequences, such as:
1. Data loss
Disruptions caused by cyberattacks, server or network outages may lead to corrupted, damaged, or stolen data. Unanticipated downtime, like server outages, can potentially expose sensitive data or generate security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit to obtain unauthorised access, which can be detrimental to business operations.
2. Safety hazards
Downtime due to malfunctioning equipment can pose safety hazards for workers. This can lead to accidents and injuries, potentially resulting in increased insurance costs, legal liabilities, and damage to the manufacturing company's reputation. Safety hazards caused by downtime can also lead to a loss of employee morale, as workers may feel that their safety is not a priority.
3. Lost productivity
Downtime stemming from equipment failure or network outages renders mission-critical systems inaccessible for use, rendering workers unable to perform their tasks, resulting in inventory decline, slowed supply chains, dissatisfied customers, and revenue losses.
Downtime can also negatively influence employee morale and job satisfaction, causing stress, burnout, and even job insecurity due to the possibility of layoffs or cost-cutting measures related to decreased productivity.
4. Reduced efficiency
Increased maintenance, overtime, or other expenses associated with downtime can drive up operating expenses and lead to decreased product quality and customer satisfaction, further impacting a manufacturing company's bottom line.
5. Lost business opportunities
In the highly interconnected digital landscape where businesses depend greatly on application uptime and availability, even a brief period of downtime can negatively impact a manufacturer.
Downtime can result in unsatisfactory experiences where customers cannot access the offerings and workers cannot provide support because essential tools are inoperative. Such situations can quickly deter both existing clients and potential customers.
Types of maintenance techniques in an industrial setting
So you see, maintenance is critical to ensuring that equipment and machinery operate efficiently and safely. Several types of maintenance techniques can be used to keep these systems running smoothly. We have compiled the entire list:
1. Corrective maintenance
This technique involves repairing or replacing equipment components after a failure or malfunction has occurred. It is a reactive approach, dealing with issues as they arise, and can sometimes result in higher costs and longer industrial downtimes, affecting the supply chain.
2. Reactive maintenance
This is similar to corrective maintenance, which involves addressing equipment problems as they occur without a proactive plan. This approach results in increased costs and unplanned downtime, as problems are not identified until they cause failure. Reactive maintenance may be appropriate for low-priority equipment but is not recommended for critical systems.
3. Predictive maintenance
It is an analytics-based approach that uses sensors and monitoring systems to anticipate potential equipment failures before they occur.
By analyzing data from these sources, maintenance professionals can identify patterns and trends that indicate a need for maintenance or repairs. Predictive maintenance allows for timely intervention, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
4. Risk-based maintenance
This maintenance technique prioritizes equipment and systems based on their potential impact on business operations. By focusing on high-risk assets, resources can be allocated more efficiently to reduce overall risk in an operational capacity.
5. Preventive maintenance
It is a proactive approach to equipment upkeep that involves regular inspections, servicing, and maintenance to reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures.
By performing routine checks and repairs, preventive care helps to extend the life of machinery and minimize unplanned downtime. It is particularly effective for critical equipment essential to an industrial operation's success, as it can help identify and attend to matters before they become major problems.
6. Condition-based maintenance
This relies on real-time equipment performance monitoring to determine when maintenance is required. By managing issues based on the actual condition of the machinery, condition-based maintenance optimizes maintenance schedules and resource allocation while minimizing downtime.
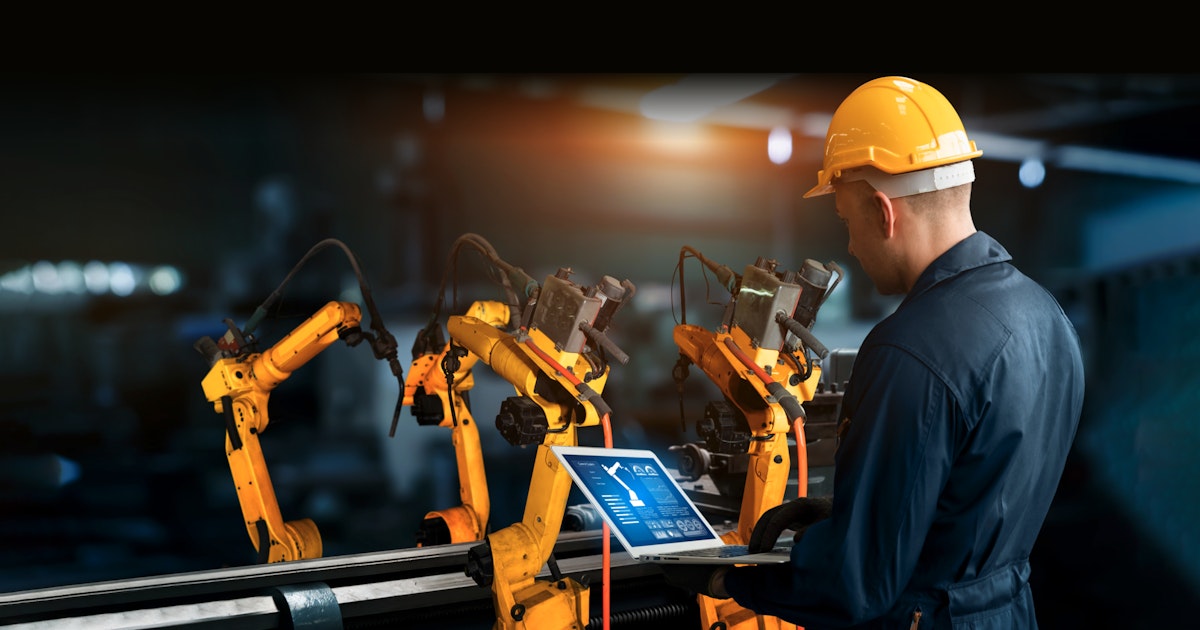
Industrial IoT solutions that can help minimize industrial downtime
IoT-based predictive maintenance is a proactive approach to minimizing industrial downtime by leveraging connected sensors,gateway connectivity, a functional dashboard and data analytics to anticipate and address equipment maintenance needs before failures occur.
This technology-focused strategy helps improve equipment performance by integrating with existing industrial setups. There are seven key ways IoT can help reduce industrial downtime using predictive maintenance.
1. Swift remote diagnostics
Remote monitoring and diagnostics capabilities of IoT-enabled devices expedite problem-solving, reducing downtime and repair costs. Real-time data on equipment performance enables remote identification and resolution of issues, enhancing the overall efficiency of the maintenance process.
2. Real-time asset monitoring
IoT sensors facilitate remote monitoring of the location and condition of equipment across factories, warehouses, or industrial sites. This capability enables manufacturers to manage their assets more effectively by delivering real-time equipment location and status data.
It minimizes the risk of equipment loss or theft and enhances asset utilization by identifying and addressing underused equipment.
3. Proactive anomaly detection
IoT sensors provide a means to proactively monitor equipment by detecting anomalies in various parameters such as temperature, vibration, and noise levels. This equips manufacturers to identify potential difficulties early on and schedule maintenance accordingly, thus avoiding downtime and more severe damage to the equipment.
4. Predictive modeling methods
Advanced failure prediction uses algorithms to recognize patterns or trends indicative of an imminent failure or decline in performance.
This helps manufacturers transition from reactive or time-based maintenance to a more effective condition-based maintenance strategy, with maintenance activities scheduled according to the equipment's actual state instead of predetermined intervals.
By foreseeing when and where maintenance is needed, manufacturers can allocate resources more efficiently, such as streamlining maintenance personnel scheduling, procuring spare parts beforehand, and refining inventory management.
5. Real-time condition monitoring
Incorporating IoT sensors in industrial settings enables condition monitoring, transforming how maintenance is conducted. This information-guided approach empowers manufacturers to perform maintenance based on the equipment's actual state, resulting in optimized maintenance schedules and cost reductions by eliminating unnecessary servicing.
6. Data-centric predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance, a technique leveraging machine learning algorithms and data analysis, enables anticipating equipment maintenance needs. IoT sensors collect and analyze equipment performance data, identifying patterns that signal impending maintenance requirements.
This proactive approach helps avert unexpected downtime and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment by tackling obstacles before they escalate.
7. Cost-efficient maintenance management
IoT sensors contribute to cost-efficient maintenance by facilitating early identification of equipment glitches, averting expensive emergency repairs, and minimizing downtime. The real-time data gathered assists in making informed decisions about maintenance strategies, equipment replacements, and overall optimization of industrial maintenance processes.
Cutting-edge Industrial IoT Solutions and Development Services Company
Explore NowOver to you
Whether your objective is to enhance customer experiences, decrease unplanned maintenance costs, or gain better insights into equipment location and usage, IoT-based predictive maintenance solutions can be beneficial. The right technology partner, like Intuz, can seamlessly implement them for you, significantly reducing the time and investment needed.
Intuz offers a comprehensive suite of equipment, devices, and remote management tools for asset monitoring, obtaining insights and conducting predictive maintenance on critical assets across various industries. If you would like to know more about how we help manufacturers book a free consultation with us today!